OpenAI Hits $10 Billion Annual Revenue: User Growth, Income Losses, Infrastructure Investments, and the Challenge of Sustainable AI Expansion
- Jun 10, 2025
- 6 min read

1. The $10 Billion Revenue Milestone
In June 2025, OpenAI officially announced that its annualized recurring revenue had reached $10 billion, an extraordinary leap that reflects both surging global interest in artificial intelligence and rapid business execution. This milestone was achieved in just six months, effectively doubling the $5.5 billion annual run rate reported at the end of 2024. The impressive pace of growth is primarily driven by the widespread adoption of ChatGPT subscriptions and OpenAI’s API business, with revenue coming directly from individual users, professionals, and companies of all sizes.
What’s especially notable about this figure is that it excludes one-off “mega deals” with major tech partners. For instance, huge licensing agreements—such as Microsoft’s multi-year Azure commitment—aren’t part of this headline number. This means the $10 billion figure reflects the strength of OpenAI’s core recurring business, indicating a healthy base of paying users and developers actively integrating OpenAI’s technology into their products and services.
2. Revenue Trajectory: From Launch to 2025
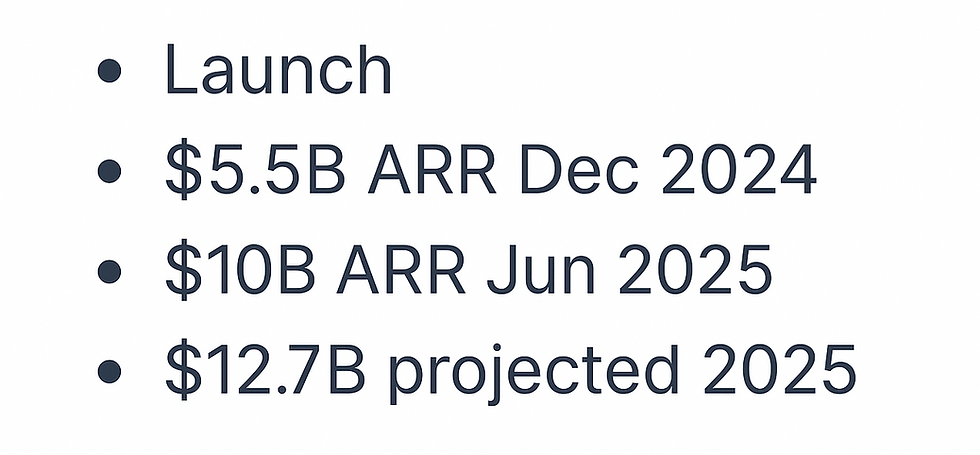
OpenAI’s rise in revenue has been almost unprecedented for a technology company. In 2023, the company generated about $1.6 billion, primarily on the back of its new paid ChatGPT Plus subscriptions and early partnerships.
By 2024, this figure had more than doubled to nearly $4 billion, as OpenAI expanded its offerings to enterprise clients and rolled out more advanced versions of its models.
2025 has proven to be a watershed year, with OpenAI on track to close out with more than $12 billion in revenue if current trends hold. Several key factors fueled this momentum: the introduction of tailored business plans such as ChatGPT Team, the launch of GPT-4o (a faster, more cost-effective model), and a major expansion in API features that allow businesses to build their own applications on OpenAI’s platform. This broadening of the product line helped OpenAI attract a much wider audience—ranging from individual freelancers to multinational corporations—while also deepening engagement with existing customers.
3. User Growth and Business Adoption
OpenAI’s user base has grown at an equally impressive rate. As of early 2025, more than 500 million people worldwide use ChatGPT and other OpenAI products every week, a remarkable jump from around 180 million nine months prior. This isn’t just consumer adoption: the number of organizations using OpenAI’s services has surged, with over a quarter-million businesses now actively deploying AI-powered tools in their operations.
Industries adopting OpenAI’s technology most quickly include finance, software development, media, education, and healthcare. Businesses are leveraging ChatGPT for everything from customer service automation and internal knowledge management to advanced data analysis and creative content generation. Partnerships with major corporations and tailored offerings for regulated industries have made it easier for companies of all sizes to integrate AI into core workflows.
4. Fundraising and Valuation
To support both explosive growth and immense infrastructure needs, OpenAI has moved aggressively to raise new capital. In 2025, the company is negotiating with a mix of major technology investors, sovereign funds, and institutional backers, with some discussions targeting up to $40 billion in new funding. If successful, this would place OpenAI’s valuation near the $300 billion mark, making it one of the world’s most valuable private technology companies.
This new capital is earmarked for several purposes. A significant portion will go toward building out proprietary data centers, expanding the company’s computing resources, and investing in security and compliance measures required for enterprise customers. The fundraising also provides a cushion to weather the enormous up-front costs of developing ever more powerful AI models, as well as to stay ahead of fast-moving competitors in the global AI race.
5. Profits: The Reality Behind the Growth
Despite these blockbuster revenue numbers, OpenAI is still operating at a loss. In 2024, the company reported a net loss of approximately $5 billion, and expectations are that the loss figure could nearly double as the company scales up operations in 2025 and 2026. These losses are not the result of lackluster demand, but of the high costs required to stay at the cutting edge of AI development.
OpenAI’s leadership is clear-eyed about this dynamic. They view heavy losses as a strategic investment, choosing to spend aggressively now to build technology, capture market share, and assemble the infrastructure required for future profitability. Their own forecasts indicate that true break-even could be several years away, possibly not until annual revenues reach the $100 billion mark, and not before the end of the decade.
6. What’s Driving OpenAI’s Losses?
OpenAI’s financial outlays are substantial, and they fall into several key categories. The most significant is the cost of model training and operation. Building and refining large-scale AI models like GPT-4o requires enormous computing power, specialized hardware (such as advanced GPUs), and vast amounts of data. The costs for training a single cutting-edge model can run into the billions, and the expenses don’t stop once a model is launched—ongoing “inference” (serving user queries in real time) also carries substantial operating costs.
In addition to compute, OpenAI invests heavily in talent. The company has assembled one of the world’s leading teams of AI researchers, software engineers, and security specialists.
Attracting and retaining this talent means offering competitive salaries, equity incentives, and other benefits—another major expense.
A third component comes from OpenAI’s ecosystem approach. With the rise of the GPT Store and third-party integrations, OpenAI pays out a share of revenue to developers who create custom GPTs and applications that run on its infrastructure, further increasing the cost base.
7. Accounting for Costs: Expense vs. Capitalization
From an accounting standpoint, OpenAI follows standard U.S. practices for technology companies. Research, model development, and most software-related costs are expensed as they are incurred. This means that the vast sums spent building and training new AI models show up as immediate costs on the income statement, rather than being spread out over several years as a capital asset would be.
Occasionally, management highlights alternative metrics that exclude certain large expenditures—such as model training costs—to give investors a sense of long-term operating potential. However, official financials present the full impact of these costs, leading to the large reported net losses even in the face of impressive revenue growth.
8. When Costs Are Treated as Investments
The only major exception to the immediate-expense rule comes with physical infrastructure and equipment. When OpenAI invests in data centers, purchases specialized GPUs, or builds out its own server clusters, these are treated as capital expenditures. Such costs are added to the balance sheet as assets, then gradually reduced in value over time through depreciation. This approach spreads the cost of these investments over several years and reflects the longer-term usefulness of the infrastructure.
OpenAI’s recent moves into direct infrastructure investment—such as launching its own massive data center projects—reflect a long-term strategy to control more of its computing environment. This shift from relying primarily on partners (like Microsoft Azure) toward owning its own hardware will further increase the share of costs treated as capital expenditures going forward.
9. Competitive Position
OpenAI’s $10 billion revenue milestone puts it at the forefront of the AI industry. While some competitors are growing quickly, none have matched OpenAI’s success in building both a massive consumer audience and a profitable enterprise business. That said, the challenge isn’t just growth—it’s also managing costs. The AI industry as a whole is facing questions about the long-term sustainability of high compute spending and the ability to generate strong margins.
OpenAI’s focus on expanding its infrastructure, developing new revenue streams, and driving efficiency will all be critical to maintaining its lead as the technology landscape continues to evolve.
10. The Next Two Years: Challenges and Priorities
Looking to the near future, OpenAI faces several key challenges. The company is betting that continued innovation will enable it to stay ahead of competitors and expand its share of both the consumer and business markets. At the same time, it must address the challenge of rising costs—especially for computing hardware, energy, and advanced research—without losing the momentum that has defined its growth to date.
New product lines, including deeper business integrations, industry-specific solutions, and expanded API offerings, are expected to drive even more revenue diversity. But the company’s ability to manage spending, scale up its infrastructure, and achieve meaningful profitability will be watched closely by both investors and customers. The transition from rapid growth to sustained, efficient operations is likely to define OpenAI’s path over the next two to three years.
OpenAI’s 2025 story is one of extraordinary success paired with enormous ambition. The company is rewriting the rules for technology adoption and business scale, yet must now prove that it can combine innovation and growth with financial sustainability. Its future will be determined by its ability to strike that balance while leading the world into a new era of artificial intelligence.
_____________
FOLLOW US FOR MORE.
DATA STUDIOS




